Multi-objective optimization of departure procedure at Gimpo international airport
- Junghyun (Andy) Kim

- Dec 31, 2019
- 2 min read
Updated: Dec 9, 2024
Master thesis (Georgia Tech)
Research Motivation
Most aviation communities have increasing concerns about the environmental impacts, which are directly linked to health issues for local residents near the airport. In response to these concerns, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) issued Advisory Circular 91-53A that described two standard noise abatement departure procedure to minimize noise impact for subsonic turbo-jet aircraft. Although the FAA allows the airlines to adopt up to two noise abatement departure procedures to minimize noise impact, it was observed by several research studies that the procedures need to be customized for specific airport because the surrounding residential areas nearby the airport are different from each other.
Noise Abatement Departure Procedure (NADP)
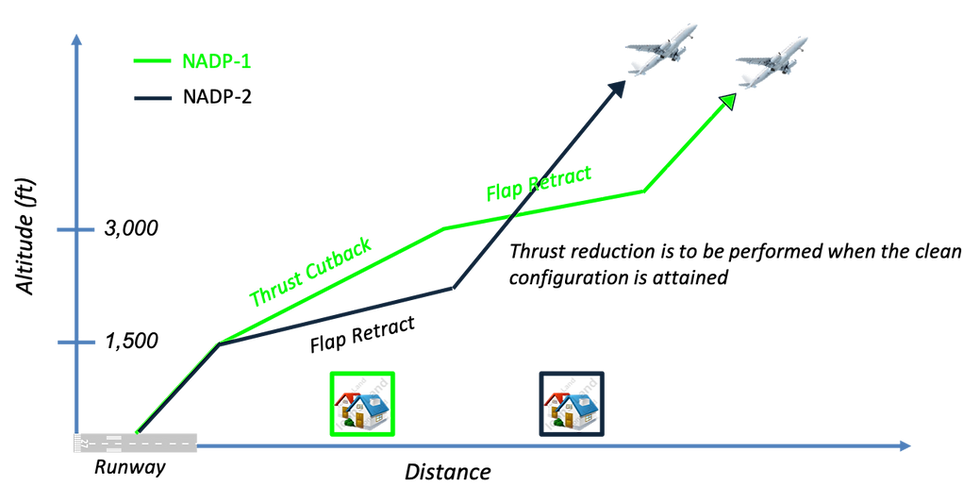
Key Idea
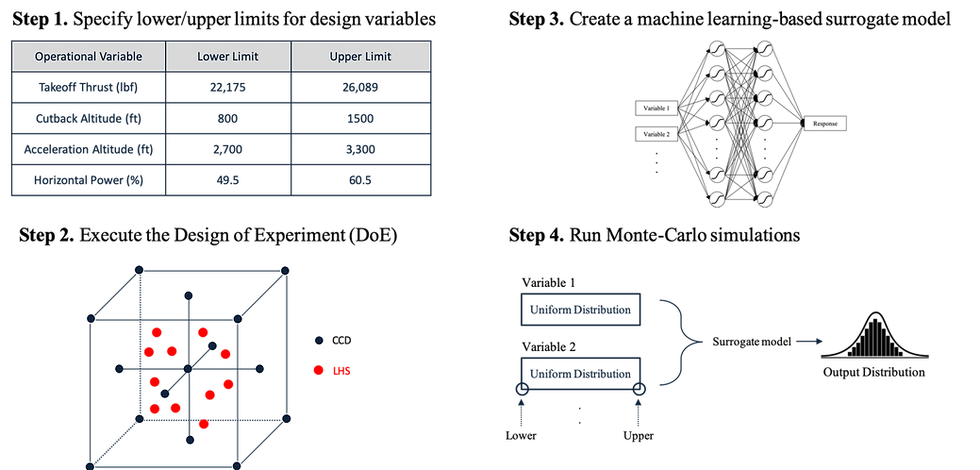
The environmental impact of different departure procedures using the Aviation Environmental Design Tool (AEDT) is analyzed. First, actual operational data are compiled at Gimpo international airport (March 20, 2017) from an open source. Two modifications are made in the AEDT to model the operational circumstances better. Second, a multi-objective optimization of departure procedure is performed for the Boeing 737-800. Four operating variables are selected and the AEDT is linked to a variety of advanced design methods.
Overview of the proposed methodology
Results
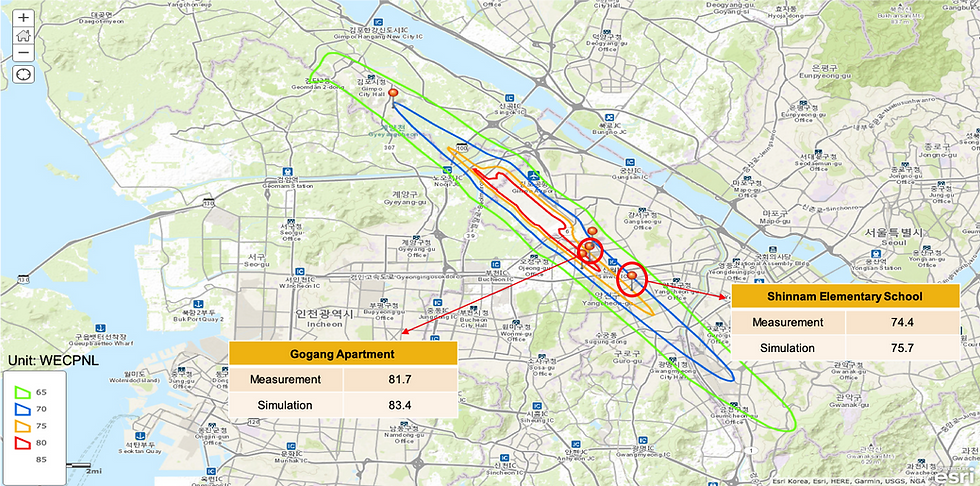
The AEDT simulations are performed according to the acquired operational procedures for a validation purpose. Simulated noise results show strong agreements with noise measurement data at specific locations near Gimpo international airport. The results from the multi-objective optimization of departure procedure at Gimpo international airport show that the noise optimum case would reduce SEL 80-dB noise exposure area by approximately 5% while the fuel burn optimum case would reduce total fuel burn by 1% relative to the baseline.
Case study (Gimpo International Airport)
Publication
Click here to access the publication.



Comments